Key Takeaways:
- BSR code is a 7-digit unique identifier assigned by the RBI to each bank branch in India.
- It helps with accurate tax reporting and filing for TDS and TCS returns.
- It is split into two parts: the first 3 digits identify the bank, and the last 4 digits specify the branch.
- You can find a branch's BSR code online or through official bank sources.
- The code plays a crucial role in ensuring regulatory compliance and efficient tax management.
The BSR (Basic Statistical Return) Code is a unique identification number assigned by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to all Indian banks. This code plays a crucial role in various financial and tax-related processes, particularly in the seamless filing of TDS/TCS returns.
Whether you’re making payments to government authorities or dealing with tax collection, understanding the BSR Code is essential for ensuring accuracy and compliance in your financial transactions. In this blog, we’ll explore what the BSR Code is, its significance, and how it impacts your financial dealings.
What is BSR code?
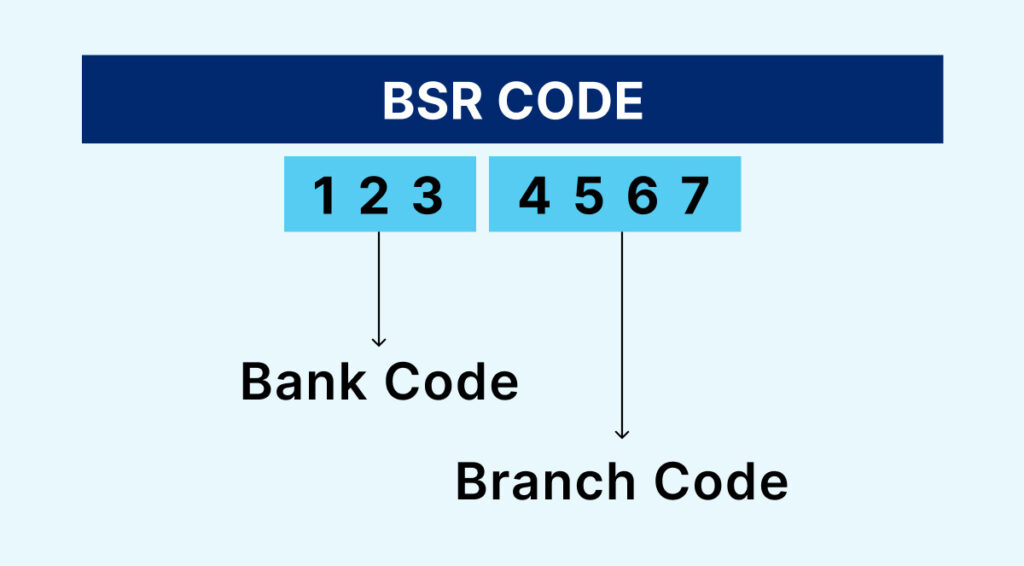
BSR (Basic Statistical Return) Code is a unique seven-digit code assigned by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to each branch of a bank in India. It consists of 7 digits, where the first 3 digits identify the bank, and the remaining 4 digits specify the particular branch of that bank. This code is essential for filing TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) and TCS (Tax Collected at Source) returns. You can typically find your BSR Code on TDS certificates and tax challans.
Here’s how the code is structured:
[4567] – Specifies the particular branch of that bank.
Bank Code: 123
[123] – Identifies the specific bank.
Branch Code: 4567
Benefits of BSR code
Simplifies Audits: Makes audits easier by providing detailed information about where tax payments were made and received.
Accurate Reporting: Helps ensure tax payments and deposits are reported correctly by showing exactly which bank branch was used.
Simpler Reconciliation: Makes it easier to match tax payments with bank records, helping to fix any mistakes quickly.
Easier Tax Filing: Streamlines filing TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) and TCS (Tax Collected at Source) returns with a unique code for each transaction.
Efficient Tax Management: Helps tax authorities keep track of tax collections and deposits from different branches and banks.
Reduces Errors: Cuts down on mistakes in financial reporting and tax filings by linking transactions to specific branches.
What Is the Purpose of BSR Code?
The BSR (Basic Statistical Return) Code serves several key purposes:
Enables foreign transactions: While enabling any foreign transaction from India, banks mandatorily asks for a BSR code.
Tax Filing: It is used to identify banks and their branches in the filing of TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) and TCS (Tax Collected at Source) returns. This ensures accurate reporting of tax payments made by individuals and businesses.
Tracking Transactions: It helps in tracking and reconciling tax payments with the respective banks and branches, facilitating accurate and efficient record-keeping.
Bank Identification: The code uniquely identifies the bank and branch where tax payments are deposited, aiding in the processing and verification of these transactions.
Regulatory Compliance: It supports compliance with regulatory requirements by providing a standardized way to report and track tax payments, as required by the Income Tax Department of India.
Pension withdrawal: Anyone availing pension facility, needs a BSR code along with their bank number to withdraw the pension amount.
Where is BSR Code Used?
BSR Code is primarily used for filing Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) and Tax Collected at Source (TCS) returns. They help banks track each tax payment and ensure this information is sent to the Income Tax Department.
You can find the BSR Code on:
- TDS Certificates: Documents showing the amount of tax deducted.
- Challan Identification Number (CIN): A unique number for each payment challan.
- OLTAS Challans: Forms and details related to tax payments.
Classification of BSR Code
- BSR 1: Half-Yearly Return Advances
- Purpose: Reports advances provided by bank branches to customers, categorized by credit limit size to assess risk and compliance.
- Reporting Frequency: Biannually (twice a year).
- Classification: Divided into two parts based on credit limits:
- Part I: For accounts with a credit limit exceeding ₹10,000.
- Part II: For accounts with a credit limit of ₹10,000 or less.
BSR 2: Half-Yearly Return Deposits
- Purpose: To report half-yearly returns on deposits made on the last Friday of June and December.
- Reporting Frequency: Semi-annually (twice a year).
- Last Friday of June and December.
BSR 3: Monthly Return Advances against Security of Selected Sensitive Commodities
- Purpose: To report advances against the security of specific commodities from head offices on the last Friday of every month.
- Reporting Frequency: Monthly.
- Reporting Source: Head Offices.
BSR 4: Bank Deposit Ownership
- Purpose: This code tracks who owns money in banks (like people, businesses, or the government). It helps banks understand their customers and the economy.
- Reporting Frequency: Collected every two months.
- Reporting Date: Last Friday of March every two years.
BSR 5: Annual Return on Bank Investments
- Purpose: To report on bank investments from the head office on the last day of March.
- Reporting Frequency: Annually.
- Reporting Source: Head Office.
BSR 6: Quinquennial Survey on Debits to Deposit Accounts
- Purpose: Studies how customers use their bank accounts and transactions.
- Reporting Frequency: Every five years.
BSR 7: Quarterly Survey on Deposits and Bank Credit
- Frequency: Quarterly, in June, September, December, and March.
- Purpose: Monitors the overall state of the banking sector by tracking deposits and loans.
- Data Points: Includes total deposits and loans.
| BSR Code | Purpose | Reporting Frequency | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| BSR 1: Half-Yearly Return Advances | Reports advances provided by bank branches, categorized by credit limit size to assess risk and compliance. | Biannually (twice a year) |
|
| BSR 2: Half-Yearly Return Deposits | Reports half-yearly returns on deposits made on the last Friday of June and December. | Semi-annually (twice a year) | Reporting Date: Last Friday of June and December. |
| BSR 3: Monthly Return Advances against Security of Selected Sensitive Commodities | Reports advances against specific commodities from head offices. | Monthly |
|
| BSR 4: Bank Deposit Ownership | Tracks ownership of money in banks to understand customer profiles and economic trends. | Every two months | Reporting Date: Last Friday of March every two years. |
| BSR 5: Annual Return on Bank Investments | Reports on bank investments from the head office. | Annually |
|
| BSR 6: Quinquennial Survey on Debits to Deposit Accounts | Studies customer usage of bank accounts and transactions. | Every five years | No specific reporting date provided. |
| BSR 7: Quarterly Survey on Deposits and Bank Credit | Monitors the state of the banking sector by tracking deposits and loans. | Quarterly |
|
How to Find Your Bank Branch’s BSR Code?
The tool will show you the BSR code for that branch.Benefits of BSR code
Use an Online Tool:
- Go to a BSR Code Finder tool available on official or financial websites.
Enter Details:
- Type in the bank’s name, state, district, and branch name.
Get the Code:
- User experience: BSR code has subsequently enhanced the user experience by providing a seamless and easy-to-go tax payment experience.
- Data management: Introduction oF BSR code made it easier for the RBI to track and monitor the operations of all the branches of every registered bank. This saves time and improves analytical efficiency.
How It Helps:
- Saves Time: Quick and easy way to get the code without calling the bank.
- For Taxes: Needed for filing TDS and TCS returns.
- For Payments: Makes handling financial transactions easier.
Self-Assessment Tax and the Role of BSR Code
When an individual calculates their tax liability independently based on their total income and applicable tax rates, it is known as self-assessment of tax obligations. After determining the tax amount, including any available credits such as TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) and TCS (Tax Collected at Source), the tax must be paid to the government.
Steps for Self-Assessment Tax Payment:
- Calculate Tax Liability: Compute the total tax due based on your income and the applicable tax rates.
- Apply Tax Credits: Factor in any tax credits or deductions, such as TDS or TCS.
- Download Tax Challan: Obtain the challan for self-assessment tax payment, which is used to remit the tax.
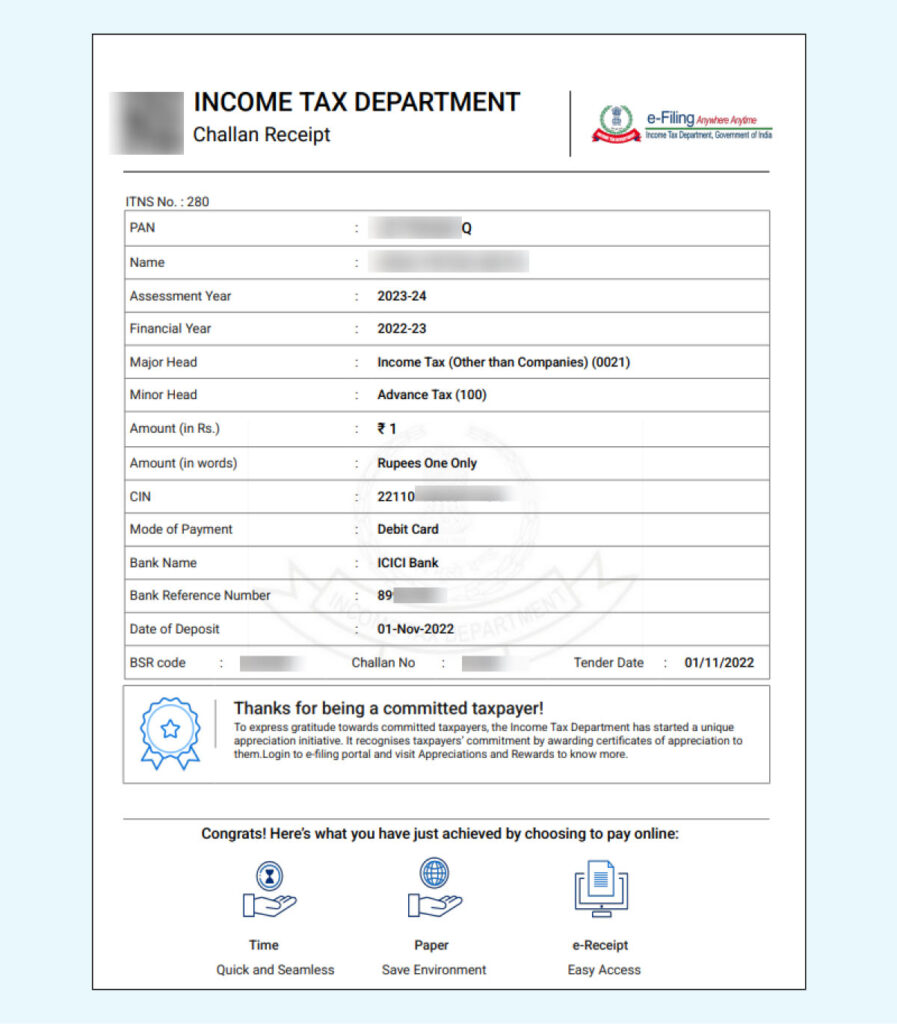
- Note BSR Code and Challan Number: The challan will provide a BSR Code and Challan number. The BSR Code identifies the bank branch where the payment was made, and the Challan number is a unique identifier for your payment.
*Make sure to keep a copy of the challan and note the BSR Code and Challan number for future reference or in case of any discrepancies. These details are essential for accurate submission and reconciliation of your tax payment with the authorities.
Filing BSR Code in the Income Tax Return (ITR)
In the Indian tax system, taxpayers are responsible for paying taxes and accurately reporting any self-assessment tax payments made. This information must be disclosed in Schedule IT of the Income Tax Return (ITR).
Steps to Report BSR Code in ITR:
- Make the Tax Payment: After calculating and paying your self-assessment tax, obtain the Challan. This document includes crucial details such as the BSR Code, Challan number, and date of payment.
- Locate Schedule IT in ITR Form: When filling out your ITR, navigate to Schedule IT, the section designated for reporting income tax payments.
- Input the BSR Code: Accurately enter the BSR Code from your Challan into the corresponding field in the ITR form. The BSR Code identifies the bank branch where the tax was paid, ensuring the payment is correctly attributed.
- Enter Challan Number and Payment Date: Along with the BSR Code, input the Challan number and date of payment as provided in the Challan.
BSR Codes vs. CIN: How They Relate and Differ
| Aspect | BSR Code | CIN (Challan Identification Number) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identifies the specific bank branch where tax payments are made. | Tracks and verifies individual tax payments made through a bank. |
| Structure | A 7-digit code: The first 3 digits represent the bank, and the last 4 represent the branch. | Composed of three parts: BSR Code, Date of Payment, and Challan Serial Number. |
| Role in Tax Payment | Essential for accurate reporting of tax-related transactions like TDS and TCS. | Ensures proper tracking and reconciliation of tax payments by the Income Tax Department. |
| Use in ITR Filing | Must be entered in the ITR to accurately report tax payments. | Must be accurately entered to avoid discrepancies in tax processing. |
| Importance | Critical for identifying the location where tax payments were processed. | Provides a unique identifier for each tax payment to verify and track transactions. |
Understanding the Link Between BSR Codes and CIN
- Role in Tax Payment Verification: When a taxpayer makes a tax payment, the bank issues a CIN that includes the BSR Code of the branch, the date of payment, and the Challan number. This CIN is crucial for the Income Tax Department to verify and reconcile the payment against the taxpayer’s records.
- Importance in ITR Filing: The BSR Code and CIN must be accurately entered into the Income Tax Return (ITR) to ensure that the payment is properly attributed to the taxpayer. Incorrect or missing information can lead to issues with tax return processing and potential penalties.
Difference Between IFSC Code and BSR Code
Here’s a comparison of IFSC and BSR Codes in table format:
Difference Between IFSC Code and BSR Code
Here’s a comparison of IFSC and BSR Codes in table format:
| Aspect | IFSC Code | BSR Code |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identifies bank branches for electronic funds transfers (NEFT, RTGS, IMPS). | Used for reporting and tracking tax-related transactions and statistical data. |
| Structure | 11-character alphanumeric code (e.g., SBIN0001234). | 7-digit numeric code (e.g., 0012345). |
| Usage | Essential for online transactions and electronic money transfers. | Primarily for tax filings and reconciliation. |
| Frequency of Use | Frequently used for every online transaction. | Used less frequently, mainly for tax-related purposes. |
| Where to Find | Available on bank statements, online banking portals, and cheque books. | Found on TDS certificates, tax challans, and bank’s official website. |
| Disclaimer: This blog is written to make it easy for readers to understand complicated processes. Some information and screenshots may be outdated as government processes can change anytime without notification. However, we try our best to keep our blogs updated and relevant. |
