TDS, or Tax Deducted at Source, is a system that deducts taxes directly from different sources of income. Its purpose is to ensure fair tax collection, prevent tax evasion, and make it easier for people to comply with tax regulations.
Table of Contents Show
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of TDS in more detail, covering its significance, procedures, and the advantages it provides to both the government and taxpayers.
What is TDS?
TDS, which stands for Tax Deducted at Source, is a process where income tax is deducted from certain payments at the time they are made. These payments can include rent, commission, professional fees, salary, and interest. Normally, the person who receives the income is responsible for paying the income tax. However, TDS ensures that the tax is deducted in advance from the payment itself. This means that the recipient gets the net amount after the tax deduction. The deducted tax amount is then adjusted against the recipient’s final tax liability. They can claim credit for the tax already deducted on their behalf.
Who Should Pay TDS?
The concept of TDS, or Tax Deducted at Source, was introduced to ensure the collection of tax at the source of income. Under this concept, the person or entity responsible for making certain types of payments to another person is required to deduct tax from the payment and deposit it into the Central Government’s account. The person from whose income the tax has been deducted (the deductee) is entitled to receive credit for the amount deducted. This can be done by referring to their Form 26AS or by obtaining a TDS certificate from the deductor. The purpose of this system is to facilitate accurate and timely tax collection and provide transparency in tax transactions.
Who Is Exempt From Paying TDS?
- Individuals or HUFs whose books are not audited.
- Payments made to RBI, Government, or mutual funds.
- Payments made to a transporter who owns 10 or fewer goods carriers and is engaged in the business of leasing, hiring, or plying goods carriage. In such cases, Form 26Q should be filled with details of non-deduction of tax along with the PAN of the payee.
- Payments made to non-resident individuals for carrying out any work.
Types of TDS
There are various types of TDS applicable in different scenarios. Some common types of TDS include:
- Salary TDS: Employers deduct TDS from the salary paid to employees based on their income tax slab rates.
- Rent TDS: TDS is deducted by individuals or entities paying rent above a specified threshold to landlords.
- Interest TDS: Banks deduct TDS on interest paid on fixed deposits, recurring deposits, and other interest-bearing accounts above a specified threshold.
- Commission TDS: TDS is deducted by businesses or individuals paying commission to agents or brokers.
- Professional Fees TDS: TDS is deducted from payments made to professionals such as doctors, lawyers, architects, and consultants.
- Dividend TDS: Companies deduct TDS on dividend payments made to shareholders above a specified threshold.
These are just a few examples of the different types of TDS. The specific type of TDS applicable depends on the nature of the payment and the provisions of the Income Tax Act.
How to file TDS Deduction?
Step 1: Visit the e-Filing Portal and Login
Go to the e-Filing portal and log in using your TAN.
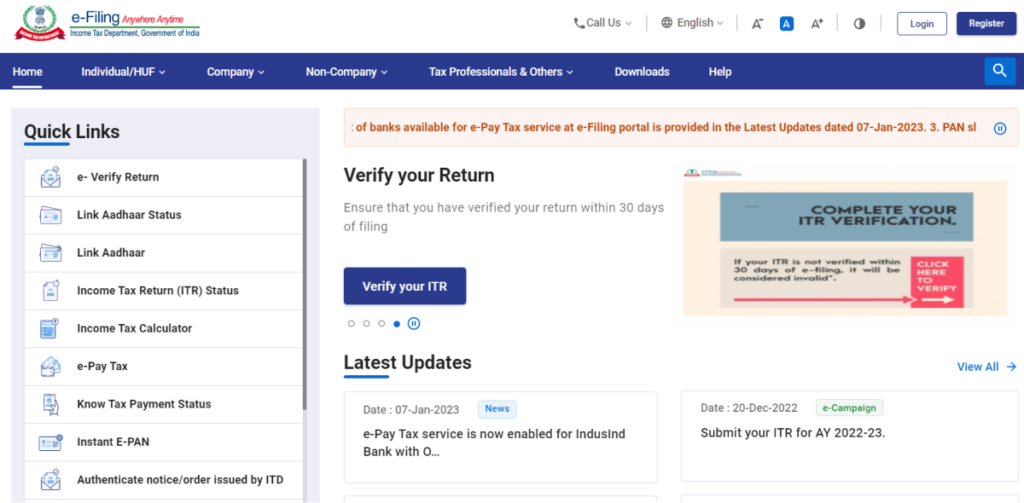
Step 2: File TDS Return Option
From the dashboard, navigate to the e-File section, then click on Income Tax Forms, and select File Income Tax Forms.
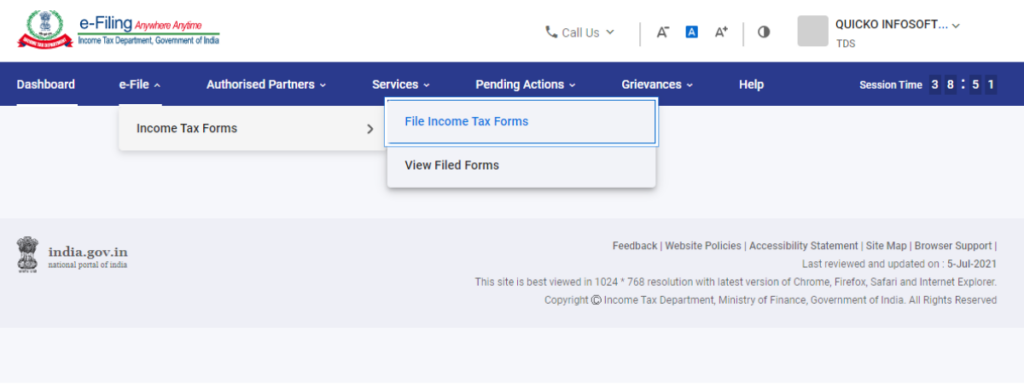
Step 3: Search the Form
Search for the specific TDS Form that you need to file.
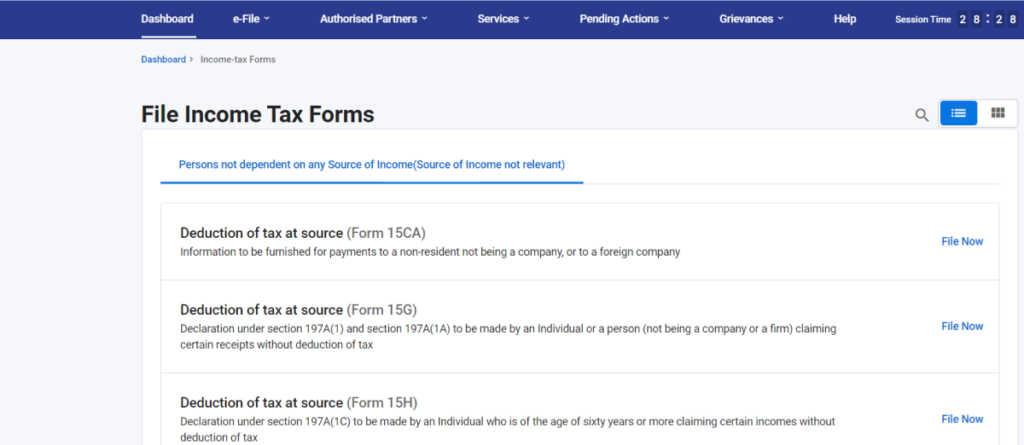
Step 4: Form TDS
Click on the “File Now” option for the Deduction of Tax at Source – TDS Form.
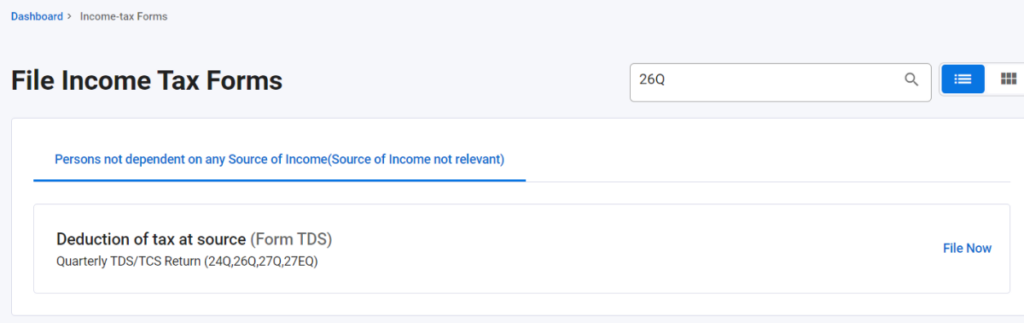
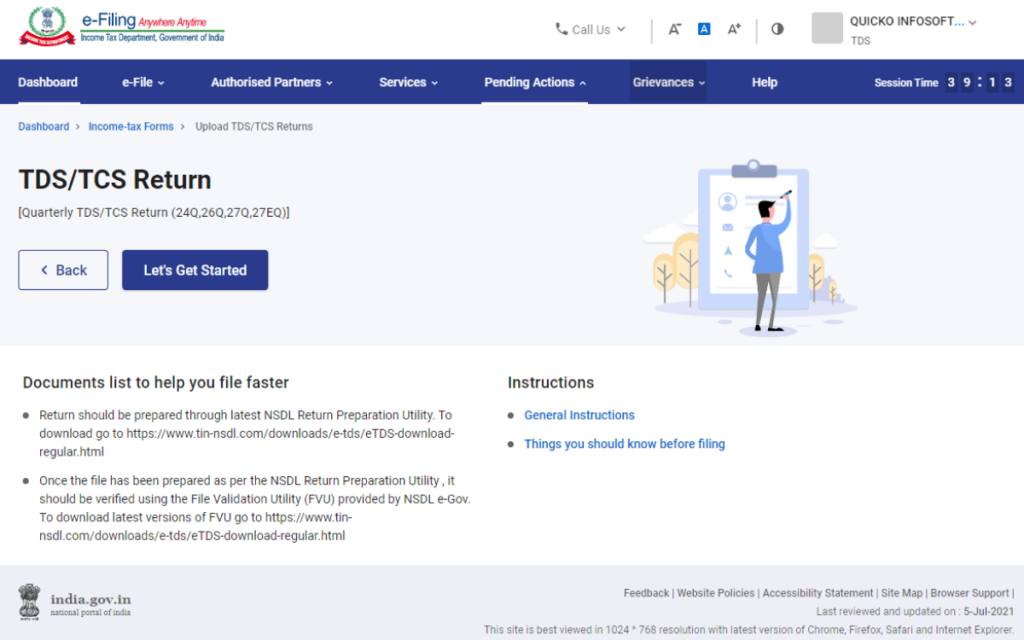
Step 5: Proceed to Upload TDS Form
Click on the “Let’s Get Started” option to proceed with uploading the TDS Form.
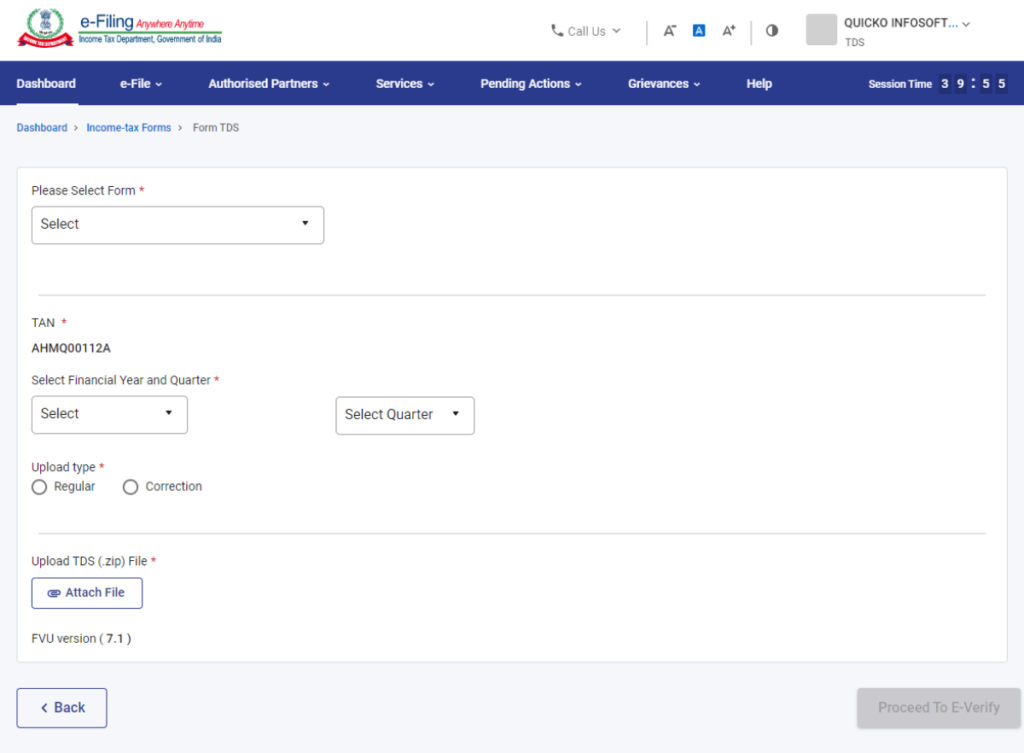
Step 6: Enter required details
Enter the necessary details, such as selecting the Form from the dropdown, entering the Financial Year and Quarter, selecting the Upload Type, and uploading the TDS zip file.
Step 7: e-Verify TDS Return
Validate the return by using the One-Time Password (OTP) sent to your registered mobile number. This completes the filing process.
After completing these steps, you will receive a success message indicating that the process is complete. If you haven’t generated your Digital Signature Certificate (DSC), you can use the Electronic Verification Code (EVC) to validate the TDS statements.
A TDS certificate, such as Form 16 or Form 16A, is a document provided to individuals in India as per TDS Section 203 of the Income Tax Act. Form 16 is given by employers to salaried employees, while Form 16A is provided for non-salaried individuals. These certificates outline the amount deducted as tax and include details on tax computation, TDS deduction, and payments.
How to Claim a TDS Refund?
- When your employer deducts more TDS than needed:
- If your salary is below the basic exemption limit, get a nil TDS certificate from the Income Tax officer.
- Give this certificate to your employer to avoid TDS deduction from your salary.
- If excess TDS has been deducted, file an Income Tax Return (ITR) to claim a refund.
- When TDS is deducted on fixed deposits:
- If your taxable income is below the threshold limit, submit Form 15G (for individuals) or Form 15H (for senior citizens) to the bank to declare no TDS should be deducted from your interest income.
- If TDS is still deducted, file an ITR to claim a refund for the deducted amount.
- For senior citizens with FD accounts:
- Senior citizens above 60 years are exempt from tax deductions on interest if it doesn’t exceed Rs. 50,000 per year.
- If your interest income exceeds the limit but your total income is within the exemption limit, submit Form 15H to the bank to declare no taxable income.
- If TDS is still deducted, file an ITR to claim a refund.
Make sure to provide accurate bank details in your ITR to receive the refund in a timely manner. If you believe that excess TDS has been deducted, filing an ITR is necessary to claim the refund.
What Are the Advantages of TDS?
- Encourages Tax Compliance: TDS ensures people fulfill their tax obligations and discourages tax avoidance.
- Steady Revenue for Government: TDS provides a consistent and reliable source of revenue for the government.
- Convenient for Payees: TDS automatically deducts the tax liability, making it convenient for individuals and businesses.
- Reduced Burden on Tax Agencies: TDS reduces the burden on tax-collection agencies by shifting the responsibility of tax deduction to the payers.
TDS Payment Deadline
The due dates for filing TDS are
| Quarter ending | Due date for filing of TDS return (Both for Government and other Deductor) | Due date for filing of TCS return |
|---|---|---|
| 30th June 2023 | 31st July 2023 | 15th July 2023 |
| 30th September 2023 | 31st October 2023 | 15th October 2023 |
| 31st December 2023 | 31st January 2024 | 15th January 2024 |
| 31st March 2024 | 31st May 2024 | 15th May 2024 |
If you fail to pay TDS after the due date, you will be liable to pay a late filing fee as per Section 234E. This fee is calculated at a rate of ₹200 per day until it reaches the same amount as the TDS return filing
Disclaimer: This blog is written to make it easy for readers to understand complicated processes. Some information and screenshots may be outdated as government processes can change anytime without notification. However, we try our best to keep our blogs updated and relevant.