Voting is the foundation of democracy in India. In India, every citizen has the right and responsibility to participate in it. In this blog, we will discuss the importance of voting, how to get a voter ID card, who is eligible to vote, and the significance of making informed choices. By understanding these key aspects, we can actively contribute to shaping our nation’s future and fulfill our duty as responsible citizens.
What is Voting?
Voting is a process where eligible individuals express their preference for a particular candidate, option, or decision in an election. This is done by using an electronic voting system or ballot paper voting. The candidate who receives the most votes is declared the winner, and this plays a crucial role in determining who will represent a community, region, or country, as well as the outcome of important decisions
Importance of Voting in India
- Voting is the cornerstone of democracy and plays a crucial role in shaping the political landscape of India.
- It allows citizens to exercise their right to choose their representatives and participate in the decision-making process.
- Through voting, individuals have the power to hold their elected officials accountable for their actions and policies.
- Voting ensures a fair and transparent electoral process, promoting social and political equality.
- It helps in establishing a government that reflects the will and aspirations of the people.
- By voting, citizens have the opportunity to voice their opinions on various issues and contribute to the development of the nation.
- Voting empowers marginalized sections of society, allowing them to have a say in matters that affect their lives.
- It promotes the growth of a responsible and responsive government, as elected representatives are more likely to address the concerns of their constituents.
- A high voter turnout strengthens the legitimacy and credibility of the democratic system.
- Voting is not only a right but also a civic duty, and by exercising it, individuals actively participate in the democratic process and contribute to the overall progress of the country.
Who Can Vote in India?
In India, the right to vote is granted to all citizens who meet certain criteria. Here is an overview of who can vote in India:
- Citizenship: Only Indian citizens are eligible to vote in elections. Non-citizens, including foreign nationals and Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), are not allowed to vote.
- Age Requirement: The minimum age to vote in India is 18 years. Any citizen who has reached this age or will reach it on or before the qualifying date specified by the Election Commission is eligible to vote.
- Electoral Rolls: To be eligible to vote, citizens must have their names included in the electoral rolls (voter list) of their respective constituencies. The Election Commission prepares and updates these rolls periodically.
- Residence: Individuals must be residents of the constituency where they wish to vote. They should have a permanent address or a temporary residence of at least six months in that constituency.
- Mental Soundness: Individuals must be mentally sound and capable of making their own decisions in order to vote.
- Disqualification: There are certain circumstances that may disqualify a person from voting, such as being of unsound mind, being disqualified by law due to criminal offenses, or being declared as bankrupt.
Note: It is important to note that while the above criteria generally apply, there may be specific rules and requirements set by the Election Commission for each election, which citizens need to adhere to in order to exercise their right to vote.
Who Can’t Vote in India?
Certain individuals are not eligible to vote in India. Here are some categories of people who cannot vote:
- Non-citizens: Non-Indian citizens, including foreign nationals and Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), are not allowed to vote in Indian elections.
- Minors: Individuals below the age of 18 are not eligible to vote. The minimum voting age in India is 18 years.
- Disqualified Individuals: People who have been disqualified from voting due to specific legal provisions, such as those convicted of certain criminal offenses or declared bankrupt, may be disqualified from voting.
Note: It is important to note that the Election Commission of India determines the eligibility criteria for voting, and there may be additional rules or exceptions depending on specific circumstances and legal provisions.
Also Read: Check Your Name in Voter List by SMS and Helpline?
How to Vote in India?
To vote in India, citizens need to follow certain steps and procedures. Here is a general guide on how to vote in India:
- Eligibility Check: Ensure that you meet the eligibility criteria to vote, which is mentioned above.
- Voter Registration: If you are not already registered as a voter, you need to apply for voter registration. You can do this by filling out Form 6, available online on the official website of the Election Commission of India or at Electoral Registration Offices. Submit the form along with the required documents, such as proof of age, address, and identity.
- Obtaining Voter ID Card: Once your application is processed and approved, you will receive a voter ID card, also known as the Electors Photo Identity Card (EPIC). The voter ID card serves as proof of your identity and is required to vote.
- Checking Voter List: Before an election, check the voter list to ensure that your name is included. The voter list is usually available online on the official website of the Chief Electoral Officer of your state or can be checked at Electoral Registration Offices.
- Polling Station Information: Find out the location of your designated polling station, as mentioned in the voter list. Polling stations are usually set up in schools, community centers, or government buildings. The Election Commission may also provide the option of finding your polling station online or through a helpline number.
- Voting Day: On the designated voting day, go to your assigned polling station during the specified voting hours. Carry your voter ID card or any other valid photo identification document, such as a passport or driving license.
- Queue and Verification: Join the queue at your polling station and wait for your turn. When your turn comes, present your identification document to the polling officials for verification. They will cross-check your details with the voter list and mark your finger with indelible ink.
- Casting Your Vote: Enter the voting booth and press the button or use the Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) to cast your vote for the candidate/party of your choice. Follow the instructions provided by the polling officials.
- Verification Slip: After casting your vote, collect the verification slip from the polling officials. This slip serves as proof that you have voted.
Note: It is important to note that specific procedures and guidelines may vary slightly across different states and elections. It is advisable to stay updated with the information provided by the Election Commission of India and local authorities regarding the voting process for each election.
Secrecy and Rules for Voters:
Secrecy and rules for voters are essential aspects of the electoral process in India. Here are some key points regarding secrecy and rules for voters:
- Secrecy of Voting: The principle of secrecy ensures that a voter’s choice remains confidential. Voters have the right to cast their votes without revealing their preferences to anyone, including polling officials or other voters.
- Booth Secrecy: While voting, voters should maintain secrecy inside the polling booth by ensuring that no one else sees their marked ballot paper or how they vote.
- Prohibition on Influencing Voters: It is against the law to influence or intimidate voters in any way, including through bribes, threats, or coercion. Voters should exercise their choice freely and independently.
- Single Vote: Each eligible voter is entitled to cast only one vote in an election. Voting multiple times or impersonating someone else is illegal.
- Restricted Area: Voters are not allowed to carry cameras, mobile phones, or any other electronic devices inside the polling booth. These items may be prohibited to prevent any unauthorized recording or dissemination of voting-related information.
- Voter ID Card: Voters must carry their voter ID card or any other valid photo identification document while going to vote. This helps in verifying their identity and eligibility to vote.
- Code of Conduct: Voters are expected to adhere to the Model Code of Conduct issued by the Election Commission, which includes guidelines on fair practices, ethical conduct, and maintaining decorum during elections.
- No Campaigning: Voters should refrain from engaging in any form of campaigning or promoting a particular candidate or political party inside or near the polling booth. Electioneering activities are not allowed within a certain radius of the polling station.
- Queue Discipline: Voters are expected to follow the instructions of polling officials, maintain discipline, and wait patiently in the queue for their turn to vote.
- Compliance with Election Laws: Voters should comply with all relevant election laws, regulations, and guidelines issued by the Election Commission and other authorities.
What Are Your Voting Rights in India?
- Everyone can vote: Every citizen aged 18 and above has the right to vote.
- Vote secretly: Your vote is confidential and nobody can know whom you voted.
- Fair elections: The Election Commission ensures that elections are unbiased and transparent.
- No discrimination: You cannot be denied the right to vote based on gender, caste, religion, or disability.
- Choose freely: You can pick from different political parties and candidates.
- Get information: You have the right to know about candidates, parties, and their plans.
- Report problems: If you see any issues during elections, you can complain and authorities will take action.
- Run for office: If eligible, you can even become a candidate and contest elections.
- Improve the system: You can be part of discussions to make the electoral process better.
How to Apply for a Voter ID in India?
To obtain a Voter ID card in India, individuals need to follow the process outlined below:
Step 1: Go to the official Voters’ Service Portal website.
Step 2: Find the ‘Forms’ section on the website and choose the appropriate form: ‘Form 6’ for residents of India or ‘Form 6A’ for NRIs. Print out the form.
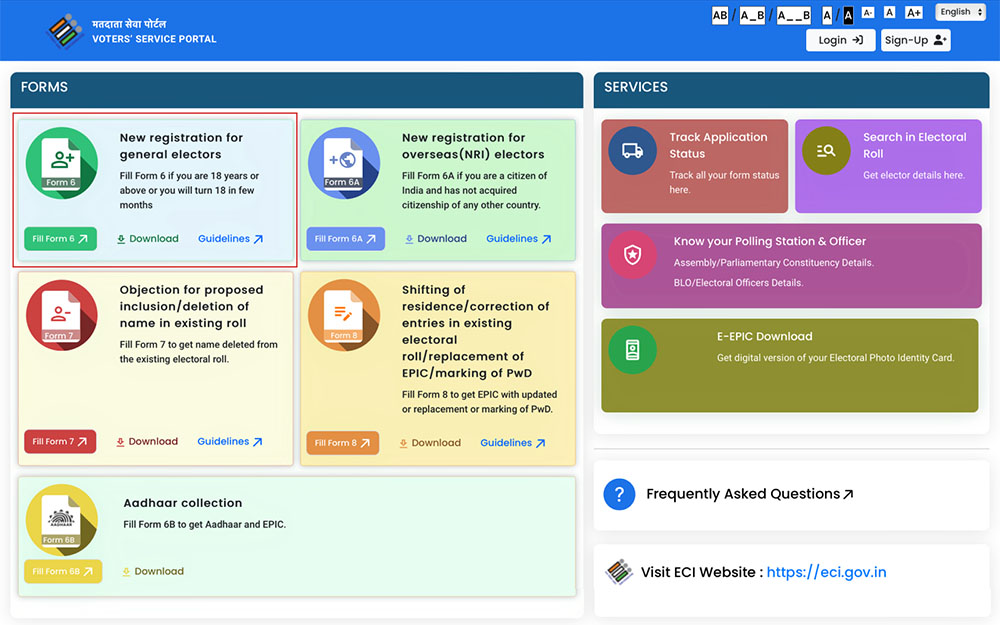
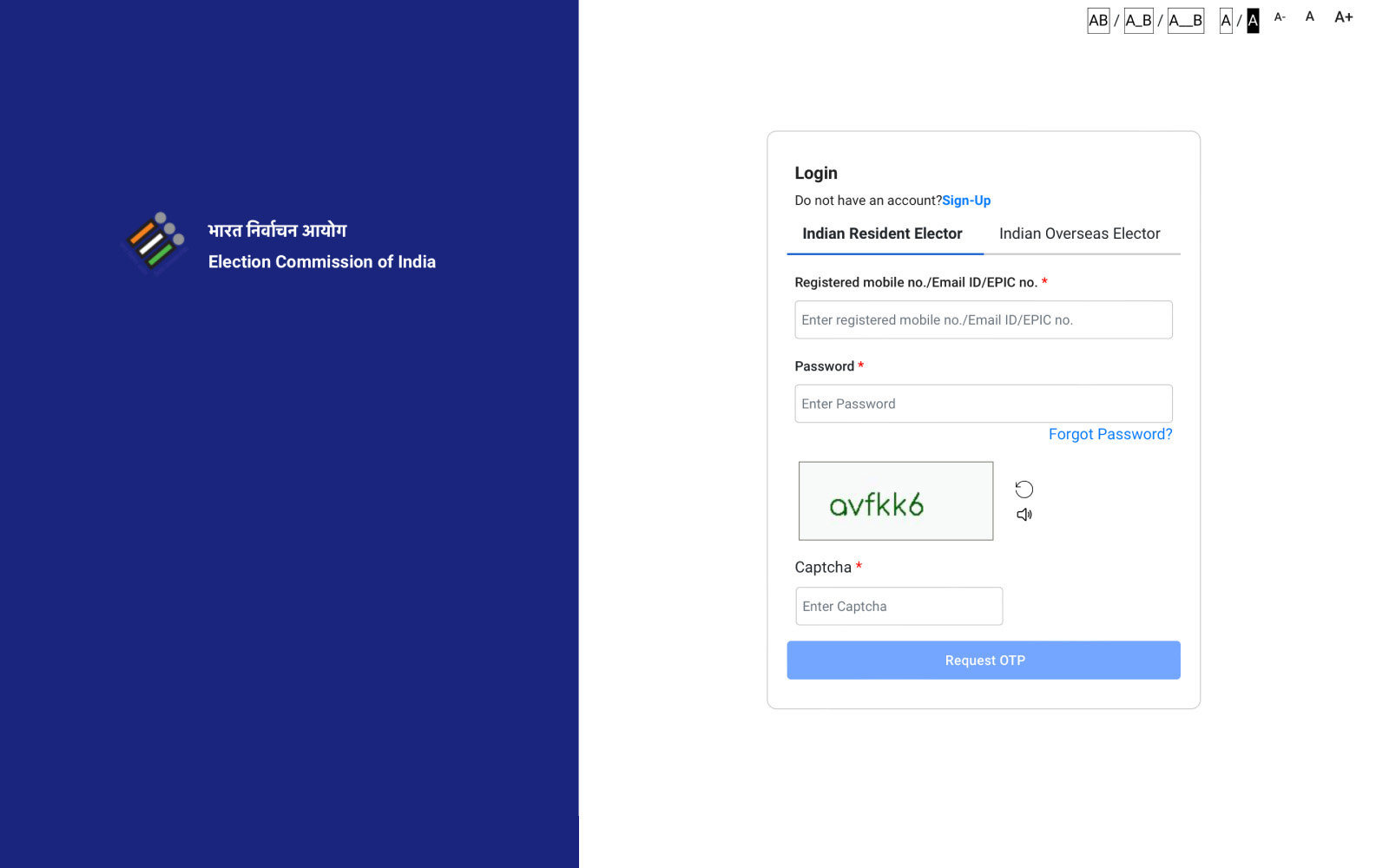
Step 3: If applying online, register by providing your mobile number, email ID, and other necessary details. If already registered, log in using your mobile number or EPIC number and the password.
Step 4: Fill in all the required details in the form and upload the necessary documents.
Step 5: Click on the “Submit” button.
Step 6: You will receive an email with a link to your personal Voter’s ID page. Here, you can track your application status. Your Voter ID card should arrive within a month.
Voting is not just a right but also a responsibility that every citizen should embrace. By voting, you can express your opinions, shape the nation’s future, and hold elected representatives accountable. Active participation in the electoral process helps uphold democracy, promote inclusive governance, and contribute to a prosperous and harmonious society.
Disclaimer
This blog is written to make it easy for readers to understand complicated processes. Some information and screenshots may be outdated as government processes can change anytime without notification. However, we try our best to keep our blogs updated and relevant.



