In the technologically growing world, the traditional methods of voting in elections have changed. One of the most significant advancements in voting in elections is the introduction of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs). With their sleek design and cutting-edge capabilities, EVMs have enhanced the way we cast our votes.
In this blog, we will learn about the details of EVMs, their functionality, advantages, and limitations. From ensuring accuracy and speed to enhancing accessibility and resource optimization, EVMs have garnered attention for their potential to streamline the voting process while maintaining transparency and security.
What is EVM?
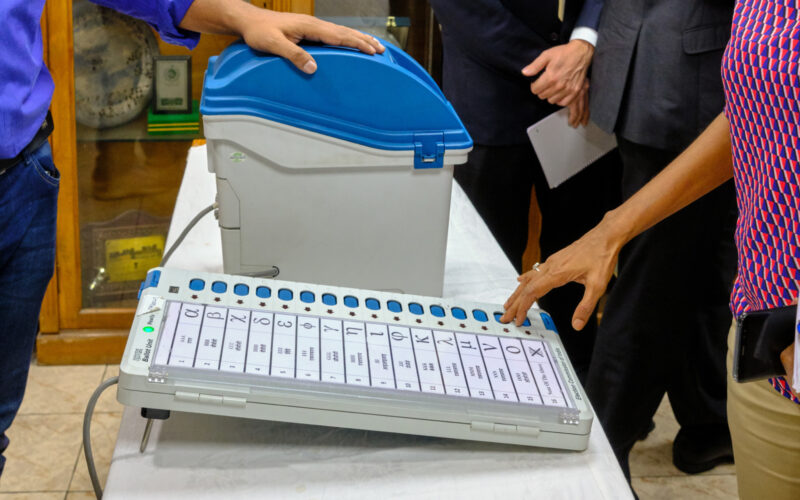
An Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) is a device used for conducting electronic voting in elections. It is a specialized electronic device designed to record votes accurately and securely. EVMs are used to replace traditional paper ballot systems in many countries around the world.
An EVM typically consists of a control unit and a balloting unit. The control unit is operated by an election official and manages the voting process, while the balloting unit is used by the voters to cast their votes. The control unit and the balloting unit are connected by a cable.
The EVM operates through a series of buttons or symbols representing different candidates or political parties. Voters press the button or symbol as per their preferred choice, and the vote is recorded electronically. The EVMs have built-in security features to prevent tampering and ensure the correctness of the voting process.
EVMs offer several advantages over traditional paper ballot systems. They can provide faster results, reduce human errors in vote counting, and eliminate problems like invalid or improperly marked ballots. EVMs also have the potential to reduce the cost of conducting elections and minimize logistical challenges associated with transporting and storing paper ballots.
However, the adoption of EVMs has also raised concerns about their security and chances of hacking or manipulation. Election authorities and manufacturers of EVMs have implemented various security measures, such as encryption and tamper-proof seals, to address these concerns and ensure the integrity of the voting process.
Also Read: Election Commission of India
Advantages of Electronic Voting Machine
- Accuracy: EVMs are designed to record votes accurately. They eliminate errors caused by manual counting and interpretation of paper ballots, reducing the chances of mistakes in the vote tallying process.
- Speed: EVMs can speed up the voting process and provide faster results compared to manual counting. The electronic recording and tabulation of votes are typically quicker, enabling more efficient elections.
- Reduced invalid votes: EVMs can help reduce the number of invalid votes. They have inbuilt features that guide voters and prevent them from casting multiple or invalid votes, such as overvoting or undervoting.
- Cost-effectiveness: In the long run, EVMs can be more cost-effective for conducting elections. While the initial investment in purchasing and maintaining EVMs may be significant, the reduction in printing, transportation, and storage costs associated with paper ballots can lead to savings over time.
- Resource optimization: EVMs minimize the need for manual labor in the counting process. This allows election officials to optimize their resources, such as human resources, time, and physical space, as the electronic recording and tabulation process requires a lesser staff and storage space.
- Transparency: EVMs provide transparency in the voting process. They typically have a display screen that shows the selected candidate or party before the vote is cast, allowing voters to verify their choice. This enhances the confidence of voters in the accuracy of their votes.
- Accessibility: EVMs can be designed to accommodate various accessibility needs, such as providing audio support for visually impaired voters or tangible interfaces for those with limited skills. This helps ensure that the voting process is inclusive and accessible to a wider range of voters.
- Environmental Impact: EVMs have a positive environmental impact compared to paper ballots. They reduce the consumption of paper and ink, leading to a decrease in deforestation and waste production associated with the printing of millions of ballot papers.
Also Read: List of Documents Required for Voter ID Card
Limitations of EVM
- Technological complexity: EVMs are sophisticated electronic devices that require technical expertise for their operation and maintenance. The complexity of the technology used in EVMs can pose challenges for election officials, particularly in regions with limited technological infrastructure or resources.
- Vulnerability to malfunction: Like any electronic device, EVMs are susceptible to technical faults, hardware malfunctions, or software errors. These issues can potentially impact the accuracy and reliability of the voting process, leading to concerns about the integrity of the elections.
- Security concerns: EVMs face security risks, including the possibility of hacking, tampering, or unauthorized access. Safeguards such as encryption and tamper-evident seals are implemented to reduce these risks, but ensuring strong security measures is crucial to maintaining the integrity of the electoral process.
- Lack of voter confidence: Some individuals may have reservations or lack trust in the accuracy and security of EVMs. The absence of tangible data or physical evidence of the vote can contribute to concerns about transparency and the ability to verify election results independently.
- Limited auditability: EVMs often lack comprehensive mechanisms for independent auditing and verification of election results. This can hamper the ability to conduct thorough post-election analysis and investigations in case of disputes or allegations of fraud.
- Cost and maintenance: While EVMs can potentially save costs in the long run, their initial acquisition and maintenance expenses can be significant. This may pose financial challenges for countries with limited resources or frequent elections.
- Software security and transparency: EVMs rely on software to function, and the security and transparency of this software are crucial for ensuring the integrity of the voting process. However, proprietary software and limited access to the source code can hinder independent verification and scrutiny, leading to concerns about potential vulnerabilities or biases.
How to Use an Electronic Voting Machine?
To use an Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) in India, follow these steps:
Step 1- Ensure that you are a registered voter and that your name appears on the electoral roll in your respective constituency. You should have a valid Voter ID card or another acceptable form of identification.
Step 2- On the day of the election, report to your assigned polling station during the designated voting hours. The details of your polling station will be communicated to you in advance through public announcements or voter information cards.
Step 3- Upon arrival, join the queue and wait for your turn. Polling officials will verify your identity by checking your voter ID card or any other acceptable identification document. Once verified, you will proceed to the voting area.
Step 4- Inside the polling booth, you will find an Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) placed on a table. There will be a polling officer who will guide you through the process, if needed.
Step 5- Approach the EVM and provide your identification to the polling officer. The polling officer will authenticate your identity and then activate the EVM for your vote.
Step 6- Look for the candidate’s name and symbol on the EVM’s control unit. Press the button next to the candidate of your choice. An indicator light or beep will confirm your selection. Ensure that you make your choice correctly as there is no option to change your vote once it is recorded.
Step 7- After selecting your candidate, the EVM will display a paper slip known as the VVPAT (Voter Verified Paper Audit Trail) for a few seconds. Verify that the VVPAT slip shows the candidate you intended to vote for. This allows you to physically confirm that your vote has been recorded as per your choice.
Step 8- Once you have verified the VVPAT slip, it will automatically be printed and dropped into a sealed box attached to the EVM. This provides a physical record of your vote while maintaining the secrecy of the ballot. Your vote is now cast.
Step 9- Leave the polling booth and the premises of the polling station.
Also Read: Link an Aadhaar Card and a Voter ID Card
Conclusion
In conclusion, Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) have brought efficiency, accuracy, and transparency to the electoral process. These sophisticated devices have transformed the way we cast our votes, replacing traditional paper ballot systems with their electronic counterparts. However, while EVMs offer numerous advantages, it is essential to address concerns related to security, transparency, and voter confidence. Implementing strong security measures, regular audits, and maintaining transparency in the software and hardware components of EVMs are crucial to ensuring the integrity and credibility of the electoral process.