For risk-averse investors seeking steady returns, fixed deposits (FDs) have long been a popular choice. Not only do they offer a secure avenue for saving and investing, but they also play a significant role in tax planning.
In order to encourage more and more people to invest, the government of India introduced tax exemptions on Fixed Deposits (FDs) for investments held for 5 to 10 years. This blog helps you understand how you can benefit from this tax exemption and build your corpus.
Income Tax Exemptions on Fixed Deposits
Exemptions under Section 80C
Under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, tax-saving FD schemes offer a tax deduction benefit. These FDs come with a lock-in period of 5 years, and deposits of up to Rs. 1.5 lakh per financial year are eligible for the deduction. The National Savings Time Deposit Account, also known as the Post Office Fixed Deposit, opened for a 5-year tenure and qualifies for the same deduction.
However, it’s essential for depositors to be aware that the interest income earned from FDs is taxable and is categorized as “Income from other sources” in the Income Tax return.
Exemptions under Section 80TTB
Senior citizens can claim a deduction on the interest earned from deposits, including fixed deposits, under Section 80TTB of the Income Tax Act. This deduction allows them to avail of up to Rs. 50,000 on the interest income from deposit accounts opened with banks, post offices, and cooperative societies engaged in banking activities.
Key Features of Tax Exemption on FDs
| Features | Tax-Saving FDs | Regular FDs |
|---|---|---|
| Income Tax Exemption | Up to Rs. 1.5 lakh investment | No specific exemption |
| Taxation of Interest | Taxable, deducted at source | Taxable, deducted at source (TDS) |
| Withdrawal and Loan Facilities | No premature withdrawals, loans, or overdrafts | Loans against deposits available |
| Interest Rate | Fixed over the five-year tenure | Varies among banks and client types |
| Interest Payouts | Fixed, no flexibility | Flexible options: monthly, quarterly, or reinvest |
| Automatic Renewal | Not available | Available |
| Account Type | Single or joint | Single or joint |
| Availability | Offered by most public and private banks | Generally offered, not common in cooperative and rural banks |
| Post Office FD Accounts | Not applicable | Transferable between post offices |
| Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) | Taxable, TDS applicable | Taxable, TDS applicable; exemption possible with Form 15G (for individuals) or 15H (for senior citizens) |
Who can Invest in FD for Tax Exemption?
- All residents of India
- Joint account holders (maybe two or more than two)
- Non-Resident Indians (NRIs)
- Societies, trusts, associations, clubs, etc.
- Sole-proprietorship companies
- Educational and religious institutions
- Partnership companies
- Minors
Benefits of Investing in FD
- Stability and Safety: FDs are considered a safe investment option as they are backed by the guarantee of the issuing financial institution. This makes them less susceptible to market fluctuations compared to other investment avenues.
- Assured Returns: FDs provide a fixed interest rate over a predetermined period, offering investors predictable returns. This feature can be particularly attractive for those seeking stable and assured income.
- Various Tenures: FDs come with a range of tenures, allowing investors to choose a period that aligns with their financial goals. This flexibility makes it suitable for both short-term and long-term investment strategies.
- Tax Benefits: Some FDs, particularly those with longer tenures, offer tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. However, it’s essential to check the specific terms and conditions to avail of these benefits.
- Senior Citizen FDs: Banks often provide higher interest rates for senior citizens on FDs, making them an attractive option for retirees seeking regular income.
It’s crucial for investors to assess their financial goals, risk tolerance, and liquidity needs before deciding on any investment. Additionally, staying informed about prevailing interest rates and terms offered by different financial institutions is essential for making informed investment decisions.
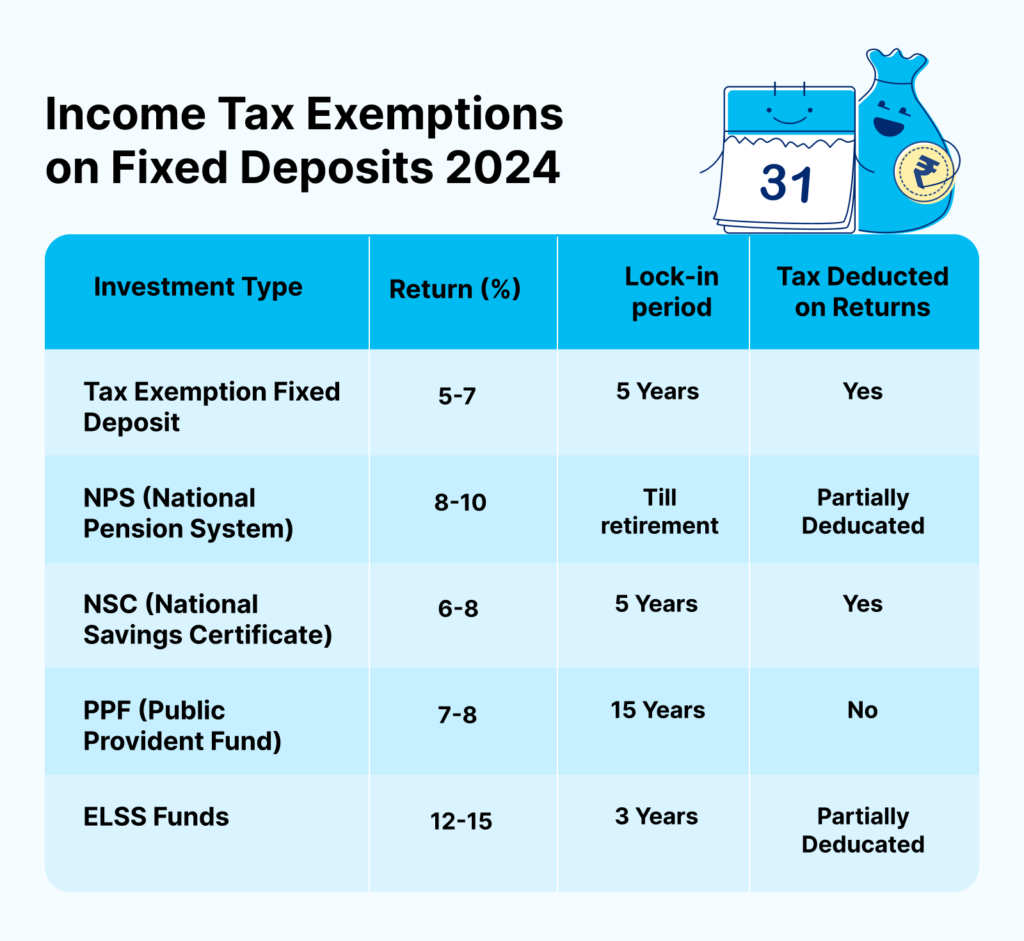
Let’s Compare FD with Other Investment Instruments
| Investment Type | Return (%) | Lock-in period | Tax Deducted on Returns |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Exemption Fixed Deposit | 5-7 | 5 Years | Yes |
| NPS (National Pension System) | 8-10 | Till Retirement | Partially Deducted |
| NSC (National Savings Certificate) | 6-8 | 5 Years | Yes |
| PPF (Public Provident Fund) | 7-8 | 15 Years | No |
| ELSS Funds | 12-15 | 3 Years | Partially Deducted |
The availability of tax-saving FD schemes and the benefits under Section 80C and Section 80TTB for specific categories of depositors offer valuable opportunities for optimizing tax planning strategies.
By taking advantage of the tax benefits available on FD interest income, investors can ensure more effective cash flow management and maximize their savings. However, it is essential to remain vigilant and adhere to the tax regulations specific to each country or jurisdiction.



