The ATM, also known as the Automated Teller Machine, is now an essential part of modern banking and our everyday routines. These machines have completely transformed the way we manage our money, allowing us to withdraw cash and carry out various financial transactions without needing to visit a bank or interact with a human teller. In this blog, we will understand more about ATMs, how to use them, benefits and a lot more.
What is ATM?
An ATM is a machine that lets you do banking tasks on your own without needing to go inside a bank. It works like a computerized kiosk. Users insert their debit or credit card, enter their PIN, and then select from a menu of available services. These services can include withdrawing cash, depositing money, transferring funds, paying bills, checking balances, and more. The ATM executes the selected transaction, dispenses cash or accepts deposits, and provides a printed receipt for record-keeping. ATMs are available in various locations, providing individuals with convenient access to banking services outside of regular banking hours.
Here are some of the common features of an ATM:
- Cash withdrawal: This is the most common ATM feature. You can withdraw cash from your checking or savings account by inserting your debit card or credit card and entering your personal identification number (PIN).
- Balance inquiry: You can check your account balance to see how much money is available in your account.
- Deposit (cash or check): Some ATMs allow you to deposit cash or checks into your account.
- Transfer funds: You can transfer money between your accounts or to another person’s account.
- Change PIN: You can change your PIN (personal identification number) at some ATMs.
Types of ATMs
ATMs come in various forms, each designed to cater to different needs:
On-Site ATMs: Located within or near bank branches, these machines are often the most secure and are directly managed by the bank.
Off-Site ATMs: Placed in convenient locations like shopping malls, airports, or gas stations, these ATMs provide accessibility outside of bank premises.
Cash Dispenser ATMs: Simpler machines that only allow cash withdrawals and balance inquiries.
White-Label ATMs: Operated by non-bank entities, these ATMs do not belong to any specific bank but allow transactions for customers of various banks.
Green Label ATMs (India): These ATMs are dedicated to agricultural transactions, such as crop insurance, loans, and subsidies.
Orange Label ATMs (India): These ATMs are used for stock market transactions, such as buying and selling stocks, mutual funds, and bonds.
Pink Label ATMs (India): These ATMs are designed for women’s safety and convenience, often located in well-lit areas and featuring security cameras.
Yellow Label ATMs (India): These ATMs are meant for e-commerce transactions.
Brown Label ATMs: These ATMs are outsourced by banks to third-party service providers, who own the hardware and lease the ATM to the bank.
Uses of Automated Teller Machine
- Main Function: The most common use of ATMs is to withdraw cash. Users can check their funds at any time, day or night, making it convenient to get money when banks are closed.
- Checking Account Balance: Users can quickly check their account balance, helping them manage their finances and confirm the availability of funds before making transactions.
- Mini-Statements: Some ATMs offer mini-statements that show recent transactions, giving users a quick overview of their account activity.
- PIN Changes: Users can change or reset their PINs at the ATM, providing a quick way to enhance security.
- Card Activation: Newly issued debit or credit cards can often be activated using an ATM, making them ready for immediate use.
Benefits of Using ATMs
- 24/7 Availability: ATMs provide round-the-clock access to banking services, which is especially useful outside regular banking hours.
- Convenience: Located in numerous and accessible locations, ATMs save time by offering quick and easy transactions.
- Reduced Wait Times: ATMs help reduce the need to visit bank branches for routine transactions, cutting down on queues and waiting periods.
- Enhanced Security: Modern ATMs are equipped with robust security measures like encryption and anti-skimming technology, ensuring safe transactions.
- Wide Range of Services: ATMs provide a broad spectrum of banking services, from basic cash withdrawals to complex financial transactions.
- Financial Inclusion: ATMs enhance financial inclusion by providing access to banking services in areas where bank branches are scarce.
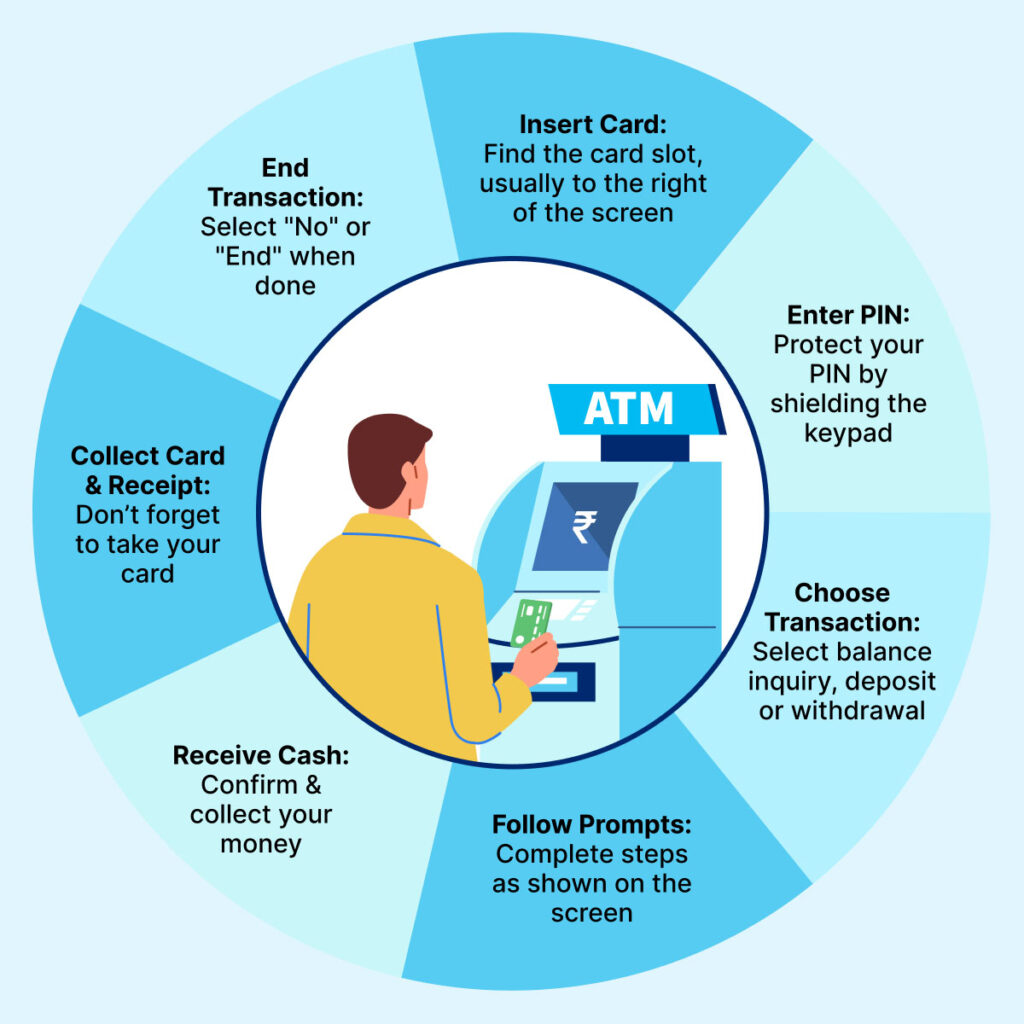
How to Use ATMs?
Here is how to use an ATM:
Before you start:
- Find an ATM: Look for an ATM that’s well-lit and in a busy area, especially if you’re using an off-site ATM. If possible, try to use an ATM that belongs to your bank’s network to avoid extra fees.
- Have your card and PIN ready: Make sure your debit or credit card is readily available, and remember your Personal Identification Number (PIN) for secure access.
Using the ATM:
- Insert your card: Locate the card slot on the ATM, usually on the right side of the screen. Most ATMs now have chip readers, so insert your card with the chip facing upwards. If it’s a magnetic stripe card, insert it with the stripe facing down towards the machine.
- Enter your PIN: The ATM will prompt you to enter your PIN. Be very careful when entering your PIN and shield the keypad with your other hand to prevent anyone from seeing it.
- Choose your transaction: The screen will display a menu of options. Select the transaction you want to perform, such as “Withdrawal,” “Balance Inquiry,” or “Deposit” (if available).
- Follow the on-screen prompts: The specific steps will vary depending on the transaction you choose.
- Receive your cash: If you confirm the withdrawal, the ATM will dispense your cash from the designated slot.
- Collect your card and receipt (optional): Don’t forget to take your card back from the ATM slot. You’ll also be prompted if you want a printed receipt for your transaction. Take it if you need it for your records.
- End the transaction: Most ATMs will ask if you want to perform another transaction. Choose “No” or “End” if you’re finished.
Remember: Be aware of your surroundings while using an ATM and never share your PIN with anyone. If you suspect something suspicious, cancel your transaction and report it to your bank immediately.
In conclusion, ATMs have made banking more accessible and convenient for everyone. They provide a quick and reliable way to get cash, even when you’re away from your bank branch or outside of regular banking hours. With ATMs, you don’t have to worry about running out of cash during emergencies or on holidays. They give you the freedom to access your money anytime and anywhere, making your financial transactions easier and more convenient.
Disclaimer: The purpose of this blog is to simplify complex processes for readers’ understanding. Please note that some information and screenshots provided may become outdated or change over time. However, we strive to keep our blogs updated and relevant to provide accurate and helpful information.



