Capital Gain Bonds, also known as Section 54EC Bonds, are an important investment avenue for individuals looking to save on capital gains tax. These bonds are issued by specified financial institutions and are governed by Section 54EC of the Income Tax Act. This blog discusses capital gain bonds and explore the advantages they offer in detail.
Table of Contents Show
What is Section 54EC?
Section 54EC is a rule in the Indian Income Tax Act that helps people save on taxes when they sell property and make a profit. Here’s how it works:
- When you sell a property like land or a building, you may have to pay taxes on the profit you made, known as capital gains.
- But under Section 54EC, you can avoid paying these taxes if you invest the profit within 6 months of selling the property.
- To qualify for the tax exemption, you need to invest the profit in special bonds called 54EC bonds. These bonds are issued by certain government-backed organizations like Rural Electricity Corporation (REC) or the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI)
- The maximum amount you can invest in these bonds is INR 50 lakhs in a year.
- If you meet all the conditions, you won’t have to pay taxes on the profit you made from selling the property.
Tax-Saving Bonds Under Section 54EC for Tax Exemption
- Rural Electrification Corporation Limited or REC bonds,
- National Highway Authority of India or NHAI bonds,
- Power Finance Corporation Limited or PFC bonds,
- Indian Railway Finance Corporation Limited or IRFC bonds.
| Institution | Bonds | Maturity Period | Maximum Investment Limit | Coupon Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rural Electrification Corporation Limited (REC) | REC Bonds | 5 years | Up to ₹50 lakhs | (Specific rates not provided) |
| National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) | NHAI Bonds | 5 years | Up to ₹50 lakhs | (Specific rates not provided) |
| Power Finance Corporation Limited (PFC) | PFC Bonds | 5 years | Up to ₹50 lakhs | (Specific rates not provided) |
| Indian Railway Finance Corporation Limited (IRFC) | IRFC Bonds | 10 years | Up to ₹50 lakhs | 7.18% p.a. for QIBs, Corporates, and High Net Worth Individuals; 7.68% p.a. for retail investors |
Note: NHAI 54 EC capital gain bond issue for 2022-23 has been closed with immediate effect. Therefore, it is important to refrain from submitting any new applications or making any further investments in these bonds on or after September 3rd, 2022.
Conditions for Section 54EC Bonds Exemption
Under Section 54EC of the Income Tax Act, the conditions for exemption are as follows:
- The investment in specified bonds must be made within 6 months from the date of sale of immovable property.
- The invested amount cannot be redeemed before a lock-in period of 5 years. Prior to April 2018, the redemption period was 3 years.
- The exemption is applicable only for long-term capital gains made from the sale of immovable property, such as land or building.
- The maximum amount eligible for exemption is Rs. 50 lakh.
How to Invest in 54EC Bonds?
To invest in tax-saving bonds, follow these steps:
Step 1: Download the bond form from the respective issuer’s website.: REC bonds, PFC bonds, and IRFC bonds.
Step 2: On the download page, choose the “direct” option.
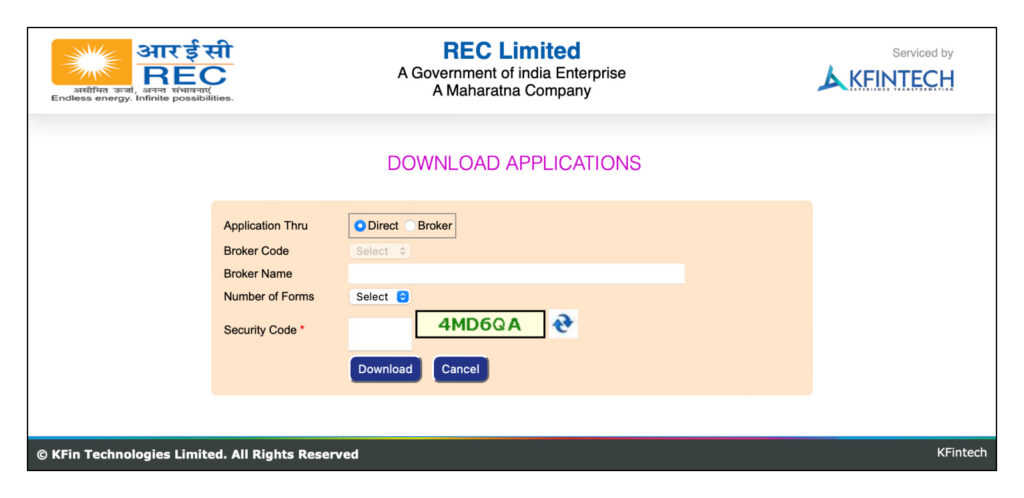
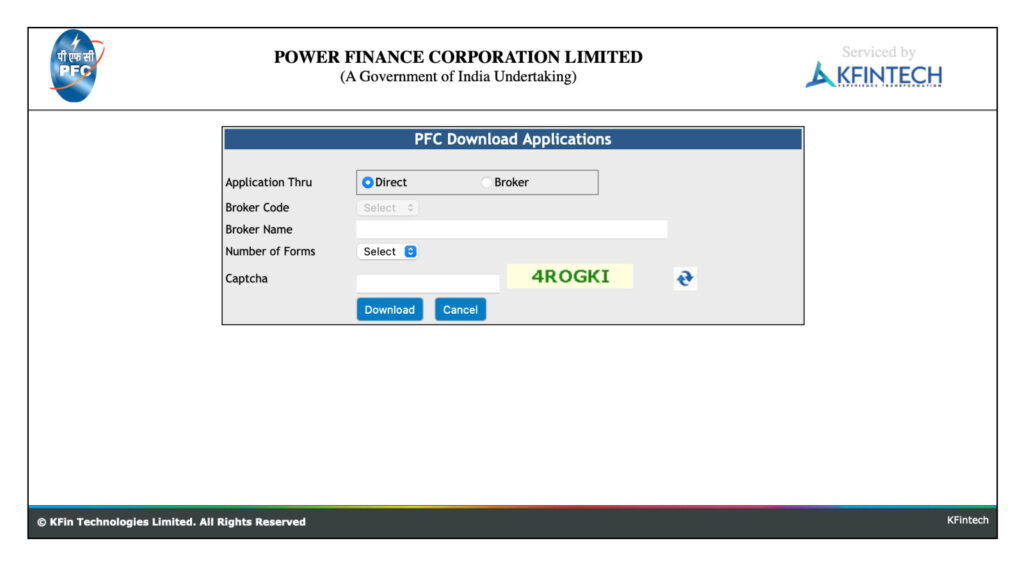
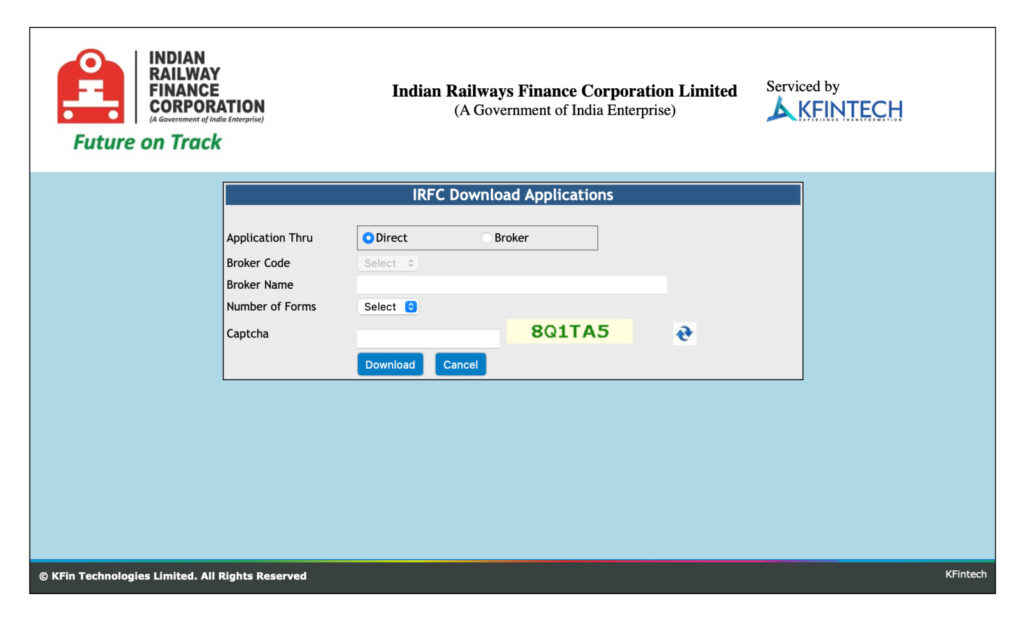
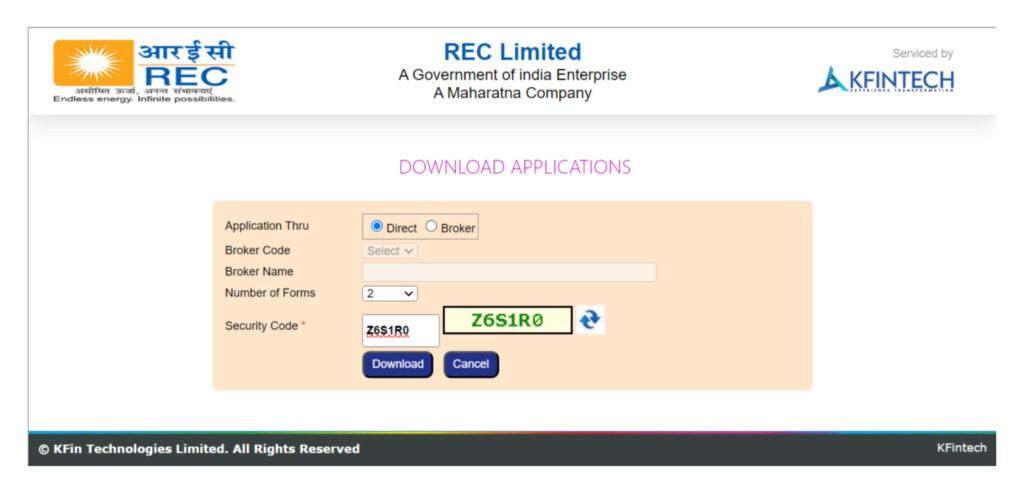
Step 3: Select the number of forms you need and enter the captcha.
Step 4: Download the form in ZIP format.
Step 5: Unzip and extract the form.
Step 6: Print the form and fill it out as per the provided instructions.
Step 7: Visit one of the designated branches of collecting banks such as Axis Bank, Canara Bank, State Bank of India, HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, IDBI Bank, IndusInd Bank, or Yes Bank. Bring along the completed bond form, a demand draft or an account payee cheque, and any required documents. Make sure to attach all the necessary documents to your application before submitting it at the bank.
Step 8: Alternatively, you can deposit the investment amount directly in the respective collection account through NEFT/RTGS. Make sure to fill out the application forms online as given on the issuer’s website and mention the UTR (Unique Transaction Reference) number in the provided space on the application form.
54EC bonds, governed by Section 54EC of the Income Tax Act, are a good investment option for individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs). These bonds offer tax savings and the opportunity to earn interest. They are backed by the government, which means they are considered safe. With a five-year lock-in period and the choice to either sell or hold the bonds, investors have flexibility in managing their investments. By investing their long-term capital gains or sales gains in 54EC bonds, individuals can save on taxes and potentially increase their overall returns.







