House Rent Allowance (HRA) is an important component of a salaried individual’s overall income. It is a benefit offered by employers to cover the costs associated with renting a house. HRA calculation considers factors like the employee’s salary structure, actual salary, and the city of residence.
Knowing the ins and outs of HRA calculation is crucial for employees to manage their taxes and financial planning. Additionally, it’s important to note organizations accept HRA as valid proof of housing expenses.
What is HRA?
HRA stands for House Rent Allowance. It is a component of an employee’s salary provided by employers to help them meet the cost of renting a home. HRA is typically granted to employees who live in rented accommodations and can be claimed as a tax exemption. The amount of HRA received may vary based on factors such as the employee’s salary, the city of residence, and the organization’s policies.
HRA Calculation Formula
The calculation of House Rent Allowance (HRA) can vary depending on the rules and regulations of the specific country or employer. In general, the HRA calculation formula involves three factors:
- Actual HRA received from the employer: This is the amount of HRA provided by the employer as a part of the employee’s salary.
- Rent paid by the employee: This refers to the actual rent paid by the employee for the accommodation they are residing in.
- Percentage of salary: This is the percentage of the employee’s salary that is considered for calculating HRA. The percentage may vary based on the specific rules and regulations.
The HRA calculation formula typically considers the least of the following three amounts:
- Actual HRA received from the employer.
- Rent paid minus 10% of salary.
- 50% or 40% of salary, depending on the city of residence (metro or non-metro).
HRA Calculator Online
An HRA calculator online is a tool that helps you calculate your House Rent Allowance (HRA) exemption for income tax purposes. It simplifies the process of determining the amount of HRA that can be claimed as a tax deduction based on various parameters such as salary, rent paid, and the city of residence.
One popular online HRA calculator is the Paytm HRA Calculator. It’s simple to use. Just enter details like your salary, basic pay, actual rent paid, HRA received from your employer, and specify if you live in a metro or non-metro city. Once you enter the required information, the calculator will give you an estimate of the HRA exemption you can claim while filing your income tax returns.
HRA tax exemption is a deduction provided by income tax laws in India. It allows salaried individuals to claim a deduction on the House Rent Allowance received from their employer if they pay rent for their accommodation. The exemption is based on factors like actual rent paid, HRA received, and salary. Proper documentation must be provided to claim this exemption
How to Calculate HRA on Paytm HRA Calculator?
Step 1: Open the official Paytm HRA calculator page.
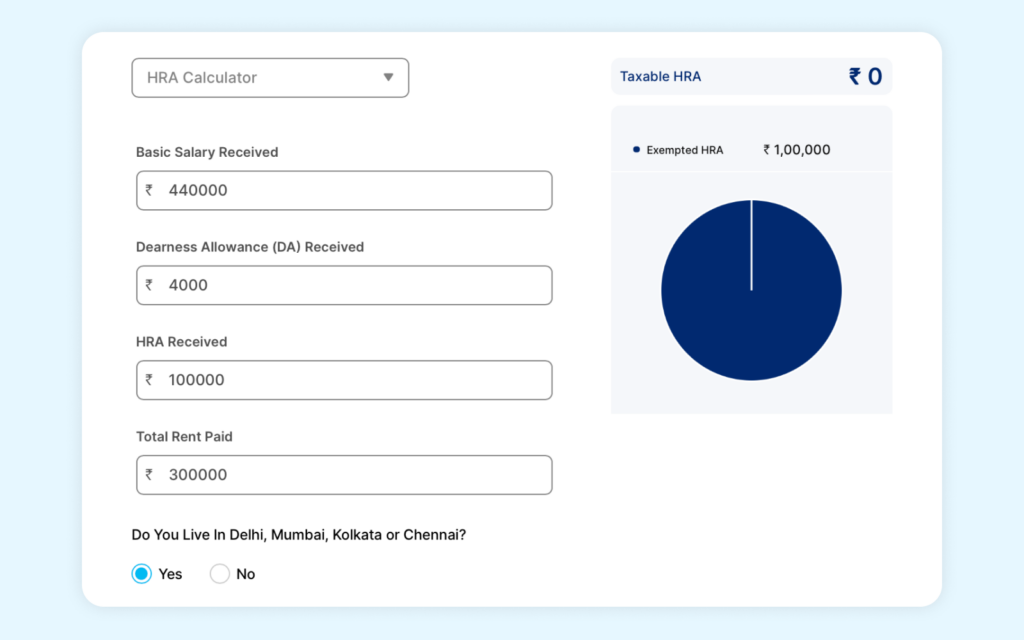
Step 2: On the page, enter your basic salary, dearness allowance, HRA received, and the total rent paid.
Step 3: Choose the city type (metro or non-metro) from the provided options.
Step 4: Once you have entered all the required details, click on the calculate button.
Step 5: The Paytm HRA calculator will process the information and calculate your HRA.
HRA Exemption Limit
The HRA (House Rent Allowance) exemption limit is determined by the income tax laws in India. The maximum amount that can be claimed as HRA exemption is the lowest of the following three amounts:
- Actual HRA received from the employer.
- Actual rent paid minus 10% of salary.
- 50% of salary for individuals residing in metro cities (40% for non-metro cities).
The lowest of these three amounts is considered for tax exemption. The remaining HRA amount is added to the taxable income and taxed accordingly.
Let’s consider an example to understand the HRA exemption limit:
Suppose you are a salaried individual receiving a monthly HRA of Rs. 15,000 from your employer. You pay a monthly rent of Rs. 20,000 for your accommodation. Your basic salary is Rs. 50,000 per month.
To calculate the HRA exemption, we need to consider the following factors:
- Actual HRA received: Rs. 15,000 per month.
- Actual rent paid minus 10% of salary: Rs. 20,000 – (10% of Rs. 50,000) = Rs. 15,000 per month.
- 50% of salary for individuals residing in a metro city: 50% of Rs. 50,000 = Rs. 25,000 per month.
In this case, the lowest of the three amounts is Rs. 15,000 per month. Therefore, the HRA exemption limit for you would be Rs. 15,000 per month or Rs. 1,80,000 per year.
Is HRA Taxable?
You are correct. HRA is not entirely taxable. The amount of HRA that can be claimed as a tax exemption is determined based on the lowest of the three amounts mentioned earlier. Any remaining portion of the HRA, if applicable, becomes taxable and is added to the individual’s taxable income.
Understanding the concept of HRA and its calculation is crucial for salaried individuals to plan their taxes effectively. By utilising an online HRA calculator, individuals can accurately determine the amount of HRA that can be claimed as a deduction, ultimately reducing their taxable income. It’s important to note that HRA rules and calculations may vary depending on the city of residence and the actual rent paid.
Therefore, utilising an HRA exemption calculator ensures precise and reliable results. By leveraging HRA effectively, individuals can optimise their tax planning strategies and achieve financial goals.
Disclaimer: Nothing on this blog constitutes investment advice, performance data or any recommendation that any security, portfolio of securities, investment product, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person. You should not use this blog to make financial decisions. We highly recommend you seek professional advice from someone who is authorised to provide investment advice.



