Many times, we all deal with unresolved grievances with our banks such as inaccurate TDS reflection, extra bank charges levied and so on. RBI introduced a customer redressal mechanism known as ‘banking ombudsman’.
Even though you have a solid understanding of the banking industry, the term “banking ombudsman” could be new to you. To precisely understand what is a banking ombudsman and what is their responsibility towards you and the nation, go through this blog thoroughly.
What is Banking Ombudsman?
A banking ombudsman means a position created by the Reserve bank of India to deal with the complaints of customers who are not satisfied with the services provided by their bank. The complaint can be raised only if the customer does not receive a reply from the concerned bank within a month from complaint date.
This position was initially established in 1995 and underwent significant revisions in 2006, addressing complaints about ATMs, debit and credit cards, unfair bank practices, and banks’ failure to provide the services they promised to provide when opening an account. The recent amendments were made up till July 1, 2017. Since RBI is in charge of designating a senior official to handle customer complaints and resentment, it is also known as the RBI Ombudsman.
In India, there are currently 22 Banking Ombudsman offices. You can file a complaint based on your bank’s jurisdiction. For instance, if you live in Bangalore, you can file a complaint with the Bangalore region’s banking ombudsman. Still, if a customer is not satisfied with the decision made by a banking ombudsman, the case is transferred to the Appellate authority i.e, Deputy governor of RBI, within 30 days after the decision is announced by a BO.
What Are the Roles and Responsibilities of a Banking Ombudsman?
You have a good understanding of the significance of a RBI ombudsman by now. With power comes responsibility. Below are some major responsibilities taken care of by a banking ombudsman.
- Handling deficiencies– A banking ombudsman handles complaints pertaining to non-acceptance of small denomination notes and coins, failure to issue drafts, pay orders, bankers’ checks, and other similar concerns.
- Acts as an arbitrator- In cases involving grievances such failing to follow the Fair Practice Code, rejecting requests to open bank accounts without a good cause, charging clients without warning, etc., a banking ombudsman serves as a mediator.
- Protects the right– The associated ombudsman ensures that the banks are adhering to all policies. He oversees the civil administration to safeguard the rights of citizens.
- Action against misconduct – An ombudsman holds discretionary powers to exercise in case of misconduct, corruption or negligence by the bank authorities.
- Investigation– An essential function of a banking ombudsman is to examine the matter. He has the authority to demand information from banking officials and compensate up to ₹20 lakhs to the resentful.
Where Is the Banking Ombudsman Appointed and Who Appoints Them?
The Reserve Bank of India appoints all banking ombudsman nationwide. Currently, there are 22 regional banking ombudsman offices, the most of which are located in capitals. The most recent one is in Jammu and Kashmir, established in April 2017.
Usually, an RBI chief general manager or general manager is designated as the ombudsman. The tenure of an Ombudsman is 3 years at a time, with the option to extend it at the end.
Who Is Eligible to Become a Banking Ombudsman?
If someone wants to act as a banking ombudsman, following is the eligibility criteria to consider:
- The concerned person should have experience in sectors like legal, banking, financial services or public administration sector.
- The person should be a person of repute.
How to File a Complaint With a Banking Ombudsman?
By now you have a clear idea of what is banking ombudsman. Now, to register a complaint with a banking ombudsman, there is a comprehensive procedure that needs to be followed.
Step 1: Contact Your Bank
Start by reporting the issue to your bank. If they don’t respond within 30 days, or if their response isn’t helpful, you can escalate your complaint.
Step 2: File a Complaint with RBI Ombudsman
If the bank doesn’t resolve the issue, you can file a complaint with the Reserve Bank of India Ombudsman (RBIO). Visit cms.rbi.org.in and click ‘File a complaint’ or call the toll-free number 14440 for assistance.
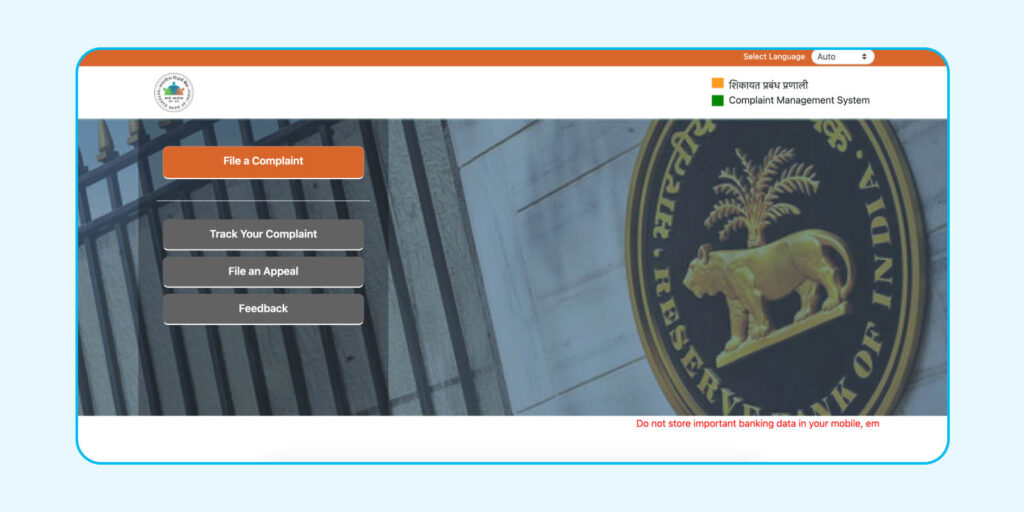
Step 3: Verify Your Details
Enter the captcha code on the site, click ‘Next,’ then add your name and mobile number. Click ‘Get OTP’ to confirm your details.
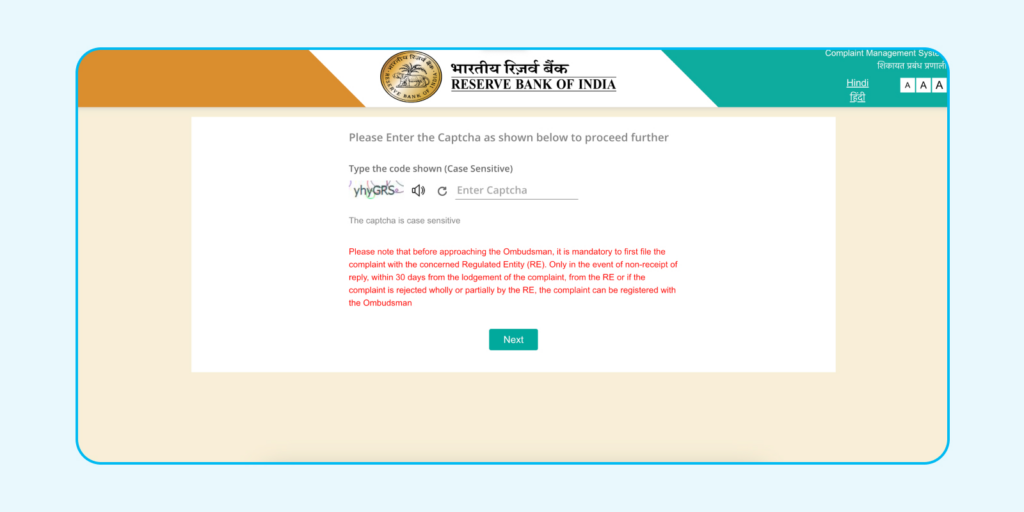
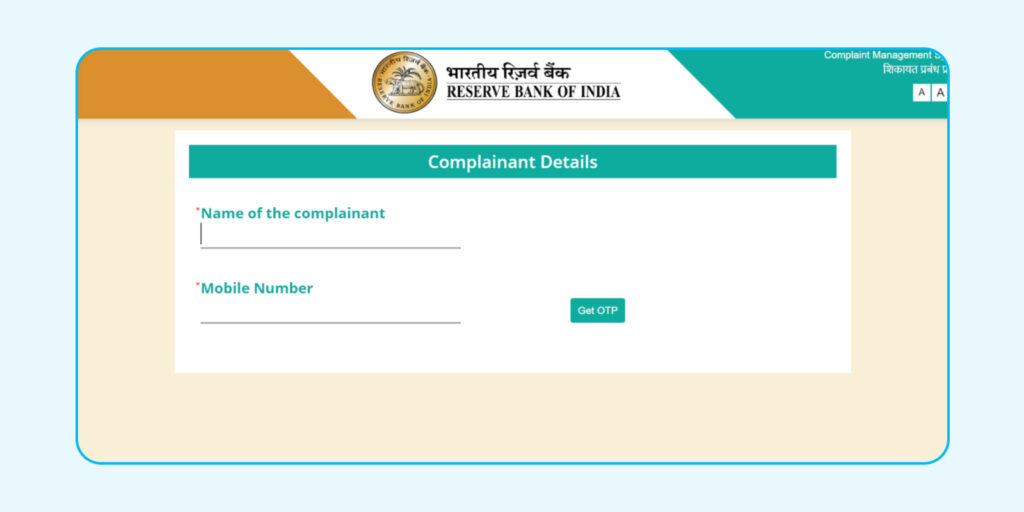
Step 4: Submit Your Complaint
In the ‘Facts of Complaint’ section, briefly explain your complaint and the outcome you’re seeking. Attach any necessary documents, like bank statements or receipts, to support your claim.
How to Track the Status of My Complaint With the Banking Ombudsman?
To track your complaint: Once submitted, you will receive an acknowledgement. The ombudsman will start working on your complaint within 30 days from submission and may reach out to you, if required. You can track your complaint online on the same portal i.e t https://cms.rbi.org.in
Step 1: Click on ‘Track Your Complaint’.
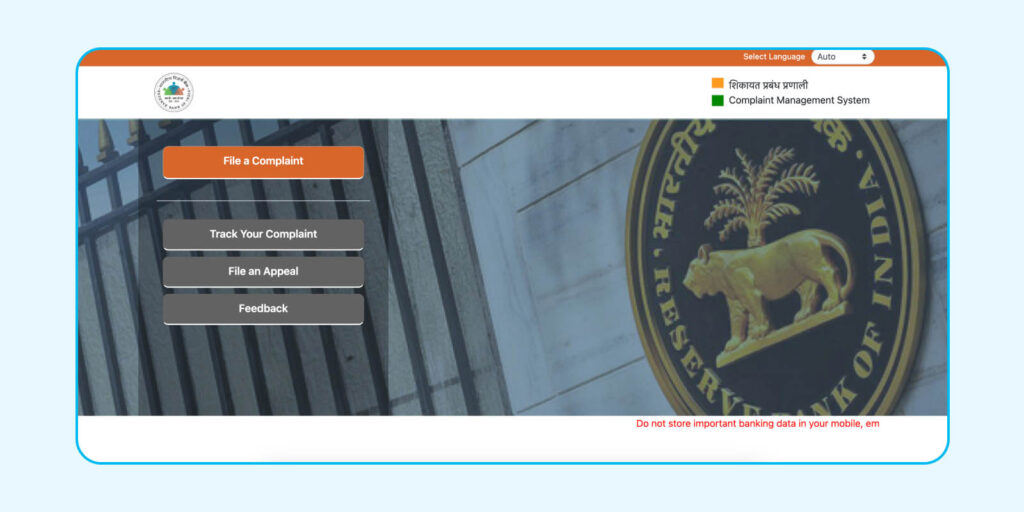
Step 2: Enter your mobile number for OTP Verification
Step 3: Next, enter your complaint number, captcha and click on ‘submit’.
Step 4: The status of your complaint will be displayed.
Types of Complaints a Banking Ombudsman Addresses
Following are the types of complaint a banking ombudsman addresses:
- Cheque and Draft Issues: Non-payment or unreasonable delays in processing cheques, drafts, or bills.
- Banking Facilities: Delay or failure to provide promised banking services (excluding loans and advances).
- Currency Acceptance: Refusal to accept small denomination notes or coins without valid reasons or charging a commission for them.
- Digital Banking: Non-compliance with RBI guidelines for mobile and electronic banking services.
- Loan Applications: Delays in sanctioning, disbursing, or processing loan applications, or refusal to accept loan applications without valid reasons.
- Operating Hours: Not adhering to the bank’s prescribed working hours.
- Deposit Issues: Delay or non-credit of deposit proceeds, non-payment of deposits, or not following RBI interest rate guidelines on deposits.
- NRI Complaints: Issues related to remittances, deposits, or other banking matters for NRIs with accounts in India.
- Account Opening: Refusal to open deposit accounts without a valid reason.
- Inward Remittances: Delay or non-payment of incoming remittances.
- Fair Practices: Failure to adhere to the bank’s fair practices code.
- Charges: Imposing fees without adequate prior notice.
- Tax Payments: Refusal or delay in accepting tax payments as required by the RBI or government.
- RBI Directives: Any other violation of RBI directives or guidelines.
- Card Operations: Non-compliance with RBI instructions regarding ATM, debit, prepaid, or credit card operations.
- Pension Disbursement: Delay or non-disbursement of pensions attributed to the bank’s actions.
- Government Securities: Issues related to the issuance, service, or redemption of government securities.
- Account Closure: Forced or delayed closure of deposit accounts without proper notice or reason.
- Recovery Agents: Non-compliance with RBI guidelines on recovery agents.
- Allied Banking Activities: Non-adherence to RBI guidelines for the sale of insurance, mutual funds, or other investment products.
- Interest Rates: Non-compliance with RBI directives on interest rates.
- RBI Instructions: Non-compliance with any other RBI directions or instructions specified for banking services.
What Are the Pre-conditions for Filing Complaints With Banking Ombudsman?
Below are some pre-conditions that must be satisfied by the customer before filing a complaint with the banking ombudsman:
Genuine Complaints Only: Ensure your complaint is genuine and not frivolous or made with inappropriate intentions.
Written Representation Required: You must submit a written complaint to the bank. If the complaint is rejected, or you receive no response within one month of the bank receiving your complaint, or if you are unsatisfied with their reply, you may proceed with further actions.
Timeliness: Complaints must be filed within one year of receiving the bank’s response to your initial complaint.
Non-Overlapping Issues: Your complaint should not involve matters currently under litigation, arbitration, or adjudication by any court, tribunal, or arbitrator, nor should it concern issues already resolved by such authorities.
Compensation Limit: Any compensatory claim is capped at INR 10 Lakhs.
Can a Banking Ombudsman Reject Your Complaint?
Yes, a banking ombudsman can reject your complaint in case of:
- No Adverse Impact: The Ombudsman finds that the complainant has not experienced any loss, damage, or inconvenience.
- Insufficient Cause or Jurisdiction Issues: The complaint lacks sufficient grounds or exceeds the monetary limits specified in Clause 12 (5).
- Frivolous Complaints: The complaint is deemed frivolous or made with inappropriate intentions.
- Lack of Diligence: The complainant does not pursue the complaint with reasonable diligence.
A banking ombudsman or RBI ombudsman is a body established by RBI to safeguard the rights of the customers and help them resolve issues. It is free of cost to reach out and lodge a complaint with a banking ombudsman regarding any above stated query.
Disclaimer: This blog is written to make it easy for readers to understand complicated processes. Some information and screenshots may be outdated as government processes can change anytime without notification. However, we try our best to keep our blogs updated and relevant.
